티스토리 뷰
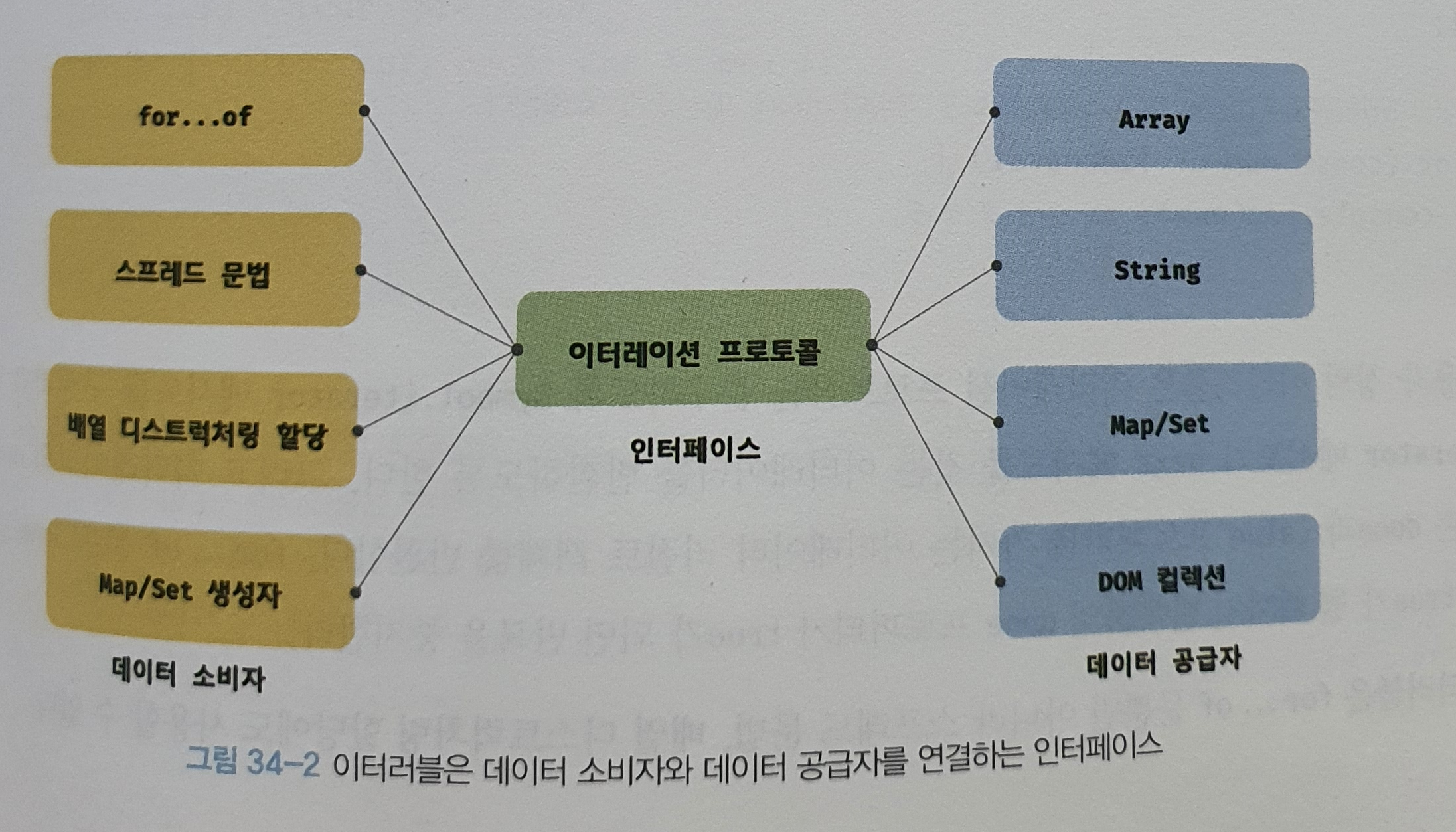
이터러블
이터레이션 프로토콜
이터레이션 프로토콜은 순회 가능한 데이터 컬렉션(자료구조)을 만들기 위해 ECMAScript 사양에 정의하여 미리 약속한 규칙이다.
이터레이션 프로토콜에는 이터러블 프로토콜과 이터레이터 프로토콜이 있다.
이터러블 프로토콜 : Symbol.iterator를 프로퍼티 키로 사용한 메서드를 직접 구현하거나 프로토타입 체인을 통해 상속 받은 Symbol.iterator 메서드를 호출하면 이터레이터 프로토콜을 준수한 이터레이터를 반환한다. 이터러블 프로토콜을 준수한 객체를 이터러블이라 한다. for...of 문으로 순회할 수 있으며 스프레드 문법과 배열 디스트럭처링 할당의 대상으로 사용할 수 있다.
이터레이터 프로토콜 : 이터러블의 Symbol.iterator 메서드를 호출하면 이터레이터 프로토콜을 준수한 이터레이터를 반환한다. 이터레이터는 next 메서드를 소유하며 next 메서드를 호출하면 이터러블을 순회하며 value와 done 프로퍼티를 갖는 이터레이터 리절트 객체를 반환한다. 이터레이터 프로토콜을 준수한 객체를 이터레이터라 한다. 이터레이터는 이터러블의 요소를 탐색하기 위한 포인터 역할을 한다.
이터러블
const isIterable = v => v !== null && typeof v[Symbol.iterator] === 'function';
// 배열, 문자열, Map, Set 등은 이터러블이다.
isIterable([]); // -> true
isIterable(''); // -> true
isIterable(new Map()); // -> true
isIterable(new Set()); // -> true
isIterable({}); // -> false
const array = [1, 2, 3];
// 배열은 Array.prototype의 Symbol.iterator 메서드를 상속받는 이터러블이다.
console.log(Symbol.iterator in array); // true
// 이터러블인 배열은 for...of 문으로 순회 가능하다.
for (const item of array) {
console.log(item);
}
// 이터러블인 배열은 스프레드 문법의 대상으로 사용할 수 있다.
console.log([...array]); // [1, 2, 3]
// 이터러블인 배열은 배열 디스트럭처링 할당의 대상으로 사용할 수 있다.
const [a, ...rest] = array;
console.log(a, rest); // 1, [2, 3]이터레이터
// 배열은 이터러블 프로토콜을 준수한 이터러블이다.
const array = [1, 2, 3];
// Symbol.iterator 메서드는 이터레이터를 반환한다. 이터레이터는 next 메서드를 갖는다.
const iterator = array[Symbol.iterator]();
// next 메서드를 호출하면 이터러블을 순회하며 순회 결과를 나타내는 이터레이터 리절트 객체를
// 반환한다. 이터레이터 리절트 객체는 value와 done 프로퍼티를 갖는 객체다.
console.log(iterator.next()); // { value: 1, done: false }
console.log(iterator.next()); // { value: 2, done: false }
console.log(iterator.next()); // { value: 3, done: false }
console.log(iterator.next()); // { value: undefined, done: true }빌트인 이터러블
Array, String, Map, Set, TypedArray, arguments, DOM컬렉션(NodeList, HTMLCollection)
for...of 문
for...of 문은 이터러블을 순회하면서 이터러블의 요소를 변수에 할당한다.
for(변수선언문 of 이터러블) {...}
for in문은 객체의 프로토타입 체인 상에 존재하는 모든 프로토타입의 프로퍼티 중에서 프로퍼티 어트리뷰트 [Enumerable]]의 값이 true인 프로퍼티를 순회하며 열거한다. 이때 프로퍼티 키가 심벌인 프로퍼티는 열거x
for of 문은 내부적으로 이터레이터의 next 메서드를 호출하여 이터러블을 순회하며 next 메서드가 반환한 이터레이터 리절트 객체의 value 프로퍼티 값을 for .. of 문의 변수에 할당한다. 그리고 이터레이터 리절트 객체의 done 프로퍼티 값이 false이면 이터러블의 순회를 계속하고 true이면 이터러블의 순회를 중단한다.
for (const item of [1, 2, 3]) {
// item 변수에 순차적으로 1, 2, 3이 할당된다.
console.log(item); // 1 2 3
}
// 이터러블
const iterable = [1, 2, 3];
// 이터러블의 Symbol.iterator 메서드를 호출하여 이터레이터를 생성한다.
const iterator = iterable[Symbol.iterator]();
for (;;) {
// 이터레이터의 next 메서드를 호출하여 이터러블을 순회한다. 이때 next 메서드는 이터레이터 리절트 객체를 반환한다.
const res = iterator.next();
// next 메서드가 반환한 이터레이터 리절트 객체의 done 프로퍼티 값이 true이면 이터러블의 순회를 중단한다.
if (res.done) break;
// 이터레이터 리절트 객체의 value 프로퍼티 값을 item 변수에 할당한다.
const item = res.value;
console.log(item); // 1 2 3
}이터러블과 유사 배열 객체
유사 배열 객체는 마치 배열처럼 인덱스로 프로퍼티 값에 접근할 수 있고 length 프로퍼티를 갖는 객체를 말한다. 이터러블이 아니므로 Symbol.itereator 메서드가 없고 for...of 문을 순회할 수 없다.
but, argumets, NodeList, HTMLCollection은 유사 배열 객체이면서 이터러블이다.
// 유사 배열 객체
const arrayLike = {
0: 1,
1: 2,
2: 3,
length: 3
};
// Array.from은 유사 배열 객체 또는 이터러블을 배열로 변환한다
const arr = Array.from(arrayLike);이터레이션 프로토콜의 필요성
사용자 정의 이터러블
이터레이션 프로토콜을 준수하지 않는 일반 객체도 이터레이션 프로토콜을 준수하도록 구현하면 사용자 정의 이터러블이 된다.
// 피보나치 수열을 구현한 사용자 정의 이터러블
const fibonacci = {
// Symbol.iterator 메서드를 구현하여 이터러블 프로토콜을 준수한다.
[Symbol.iterator]() {
let [pre, cur] = [0, 1]; // "36.1. 배열 디스트럭처링 할당" 참고
const max = 10; // 수열의 최대값
// Symbol.iterator 메서드는 next 메서드를 소유한 이터레이터를 반환해야 하고
// next 메서드는 이터레이터 리절트 객체를 반환해야 한다.
return {
next() {
[pre, cur] = [cur, pre + cur]; // "36.1. 배열 디스트럭처링 할당" 참고
// 이터레이터 리절트 객체를 반환한다.
return { value: cur, done: cur >= max };
}
};
}
};
// 이터러블인 fibonacci 객체를 순회할 때마다 next 메서드가 호출된다.
for (const num of fibonacci) {
console.log(num); // 1 2 3 5 8
}
// 이터러블은 스프레드 문법의 대상이 될 수 있다.
const arr = [...fibonacci];
console.log(arr); // [ 1, 2, 3, 5, 8 ]
// 이터러블은 배열 디스트럭처링 할당의 대상이 될 수 있다.
const [first, second, ...rest] = fibonacci;
console.log(first, second, rest); // 1 2 [ 3, 5, 8 ]최대값 max를 지정하자
// 피보나치 수열을 구현한 사용자 정의 이터러블을 반환하는 함수. 수열의 최대값을 인수로 전달받는다.
const fibonacciFunc = function (max) {
let [pre, cur] = [0, 1];
// Symbol.iterator 메서드를 구현한 이터러블을 반환한다.
return {
[Symbol.iterator]() {
return {
next() {
[pre, cur] = [cur, pre + cur];
return { value: cur, done: cur >= max };
}
};
}
};
};
// 이터러블을 반환하는 함수에 수열의 최대값을 인수로 전달하면서 호출한다.
for (const num of fibonacciFunc(10)) {
console.log(num); // 1 2 3 5 8
}만약 이터레이터를 생성하려면 이터러블의 Symbol.iterator 메서드를 호출해야 한다.
이터러블이면서 이터레이터인 객체를 생성하면 Symbol.iterator 메서드를 호출하지 않아도 된다.
// 이터러블이면서 이터레이터인 객체를 반환하는 함수
const fibonacciFunc = function (max) {
let [pre, cur] = [0, 1];
// Symbol.iterator 메서드와 next 메서드를 소유한 이터러블이면서 이터레이터인 객체를 반환
return {
[Symbol.iterator]() { return this; },
// next 메서드는 이터레이터 리절트 객체를 반환
next() {
[pre, cur] = [cur, pre + cur];
return { value: cur, done: cur >= max };
}
};
};
// iter는 이터러블이면서 이터레이터다.
let iter = fibonacciFunc(10);
// iter는 이터러블이므로 for...of 문으로 순회할 수 있다.
for (const num of iter) {
console.log(num); // 1 2 3 5 8
}
// iter는 이터러블이면서 이터레이터다
iter = fibonacciFunc(10);
// iter는 이터레이터이므로 이터레이션 리절트 객체를 반환하는 next 메서드를 소유한다.
console.log(iter.next()); // { value: 1, done: false }
console.log(iter.next()); // { value: 2, done: false }
console.log(iter.next()); // { value: 3, done: false }
console.log(iter.next()); // { value: 5, done: false }
console.log(iter.next()); // { value: 8, done: false }
console.log(iter.next()); // { value: 13, done: true }무한 이터러블과 지연 평가. 무한 수열 구현
// 무한 이터러블을 생성하는 함수
const fibonacciFunc = function () {
let [pre, cur] = [0, 1];
return {
[Symbol.iterator]() { return this; },
next() {
[pre, cur] = [cur, pre + cur];
// 무한을 구현해야 하므로 done 프로퍼티를 생략한다.
return { value: cur };
}
};
};
// fibonacciFunc 함수는 무한 이터러블을 생성한다.
for (const num of fibonacciFunc()) {
if (num > 10000) break;
console.log(num); // 1 2 3 5 8...4181 6765
}
// 배열 디스트럭처링 할당을 통해 무한 이터러블에서 3개의 요소만 취득한다.
const [f1, f2, f3] = fibonacciFunc();
console.log(f1, f2, f3); // 1 2 3스프레드 문법
스프레드 문법은 하나로 뭉쳐 있는 여러 값들의 집합을 펼쳐서 개별적인 값들의 목록으로 만든다.
스프레드 문법의 결과물은 값으로 사용할 수 없고, 쉼표로 구분한 값의 목록을 사용하는 문맥에서만 사용할 수 있다.
함수 호출문의 인수 목록
var arr = [1, 2, 3];
// apply 함수의 2번째 인수(배열)는 apply 함수가 호출하는 함수의 인수 목록이다.
// 따라서 배열이 펼쳐져서 인수로 전달되는 효과가 있다.
var max = Math.max.apply(null, arr); // -> 3
const arr = [1, 2, 3];
// 스프레드 문법을 사용하여 배열 arr을 1, 2, 3으로 펼쳐서 Math.max에 전달한다.
// Math.max(...[1, 2, 3])은 Math.max(1, 2, 3)과 같다.
const max = Math.max(...arr); // -> 3배열 리터럴의 요소 목록
concat
const arr = [...[1, 2], ...[3, 4]];
console.log(arr); // [1, 2, 3, 4]splice
const arr1 = [1, 4];
const arr2 = [2, 3];
arr1.splice(1, 0, ...arr2);
console.log(arr1); // [1, 2, 3, 4]복사
const origin = [1, 2];
const copy = [...origin];
console.log(copy); // [1, 2]
console.log(copy === origin); // false이터러블을 배열로 변환
// ES5
function sum() {
// 이터러블이면서 유사 배열 객체인 arguments를 배열로 변환
var args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments);
return args.reduce(function (pre, cur) {
return pre + cur;
}, 0);
}
console.log(sum(1, 2, 3)); // 6
// ES6
function sum() {
// 이터러블이면서 유사 배열 객체인 arguments를 배열로 변환
return [...arguments].reduce((pre, cur) => pre + cur, 0);
}
console.log(sum(1, 2, 3)); // 6
// Rest 파라미터 args는 함수에 전달된 인수들의 목록을 배열로 전달받는다.
const sum = (...args) => args.reduce((pre, cur) => pre + cur, 0);
console.log(sum(1, 2, 3)); // 6객체 리터럴의 프로퍼티 목록
// 객체 병합. 프로퍼티가 중복되는 경우, 뒤에 위치한 프로퍼티가 우선권을 갖는다.
const merged = Object.assign({}, { x: 1, y: 2 }, { y: 10, z: 3 });
console.log(merged); // { x: 1, y: 10, z: 3 }
// 객체 병합. 프로퍼티가 중복되는 경우, 뒤에 위치한 프로퍼티가 우선권을 갖는다.
const merged = { ...{ x: 1, y: 2 }, ...{ y: 10, z: 3 } };
console.log(merged); // { x: 1, y: 10, z: 3 }
// 특정 프로퍼티 변경
const changed = { ...{ x: 1, y: 2 }, y: 100 };
// changed = { ...{ x: 1, y: 2 }, ...{ y: 100 } }
console.log(changed); // { x: 1, y: 100 }
// 프로퍼티 추가
const added = { ...{ x: 1, y: 2 }, z: 0 };
// added = { ...{ x: 1, y: 2 }, ...{ z: 0 } }
console.log(added); // { x: 1, y: 2, z: 0 }디스트럭처링 할당
디스트럭처링 할당(구조 분해 할당)은 구조화된 배열과 같은 이터러블 또는 객체를 destructuring하여 1개 이상의 변수에 개별적으로 할당하는 것을 말한다. 배열과 같은 이터러블 또는 객체 리터럴에서 필요한 값만 추출하여 변수에 할당할 때 유용하다.
배열 디스트럭처링 할당
const [a, b] = [1, 2];
console.log(a, b); // 1 2
const [c, d] = [1];
console.log(c, d); // 1 undefined
const [e, f] = [1, 2, 3];
console.log(e, f); // 1 2
const [g, , h] = [1, 2, 3];
console.log(g, h); // 1 3
// 기본값
const [a, b, c = 3] = [1, 2];
console.log(a, b, c); // 1 2 3
// 기본값보다 할당된 값이 우선한다.
const [e, f = 10, g = 3] = [1, 2];
console.log(e, f, g); // 1 2 3말도 안돼
// url을 파싱하여 protocol, host, path 프로퍼티를 갖는 객체를 생성해 반환한다.
function parseURL(url = '') {
// '://' 앞의 문자열(protocol)과 '/' 이전의 '/'으로 시작하지 않는 문자열(host)과 '/' 이후의 문자열(path)을 검색한다.
const parsedURL = url.match(/^(\w+):\/\/([^/]+)\/(.*)$/);
console.log(parsedURL);
/*
[
'https://developer.mozilla.org/ko/docs/Web/JavaScript',
'https',
'developer.mozilla.org',
'ko/docs/Web/JavaScript',
index: 0,
input: 'https://developer.mozilla.org/ko/docs/Web/JavaScript',
groups: undefined
]
*/
if (!parsedURL) return {};
// 배열 디스트럭처링 할당을 사용하여 이터러블에서 필요한 요소만 추출한다.
const [, protocol, host, path] = parsedURL;
return { protocol, host, path };
}
const parsedURL = parseURL('https://developer.mozilla.org/ko/docs/Web/JavaScript');
console.log(parsedURL);
/*
{
protocol: 'https',
host: 'developer.mozilla.org',
path: 'ko/docs/Web/JavaScript'
}
*/
// Rest 요소
const [x, ...y] = [1, 2, 3];
console.log(x, y); // 1 [ 2, 3 ]객체 디스트럭처링 할당
const user = { firstName: 'Ungmo', lastName: 'Lee' };
// ES6 객체 디스트럭처링 할당
// 변수 lastName, firstName을 선언하고 user 객체를 디스트럭처링하여 할당한다.
// 이때 프로퍼티 키를 기준으로 디스트럭처링 할당이 이루어진다. 순서는 의미가 없다.
const { lastName, firstName } = user;
console.log(firstName, lastName); // Ungmo Lee위는 축약, 아래가 축약x
const { lastName: ln, firstName: fn } = user;
console.log(fn, ln); // Ungmo Lee기본값 설정
const { firstName = 'Ungmo', lastName } = { lastName: 'Lee' };
console.log(firstName, lastName); // Ungmo Lee객체에서 프로퍼티 키로 필요한 프로퍼티 값만 추출하여 변수에 할당하고 싶을때 유용
const str = 'Hello';
// String 래퍼 객체로부터 length 프로퍼티만 추출한다.
const { length } = str;
console.log(length); // 5
const todo = { id: 1, content: 'HTML', completed: true };
// todo 객체로부터 id 프로퍼티만 추출한다.
const { id } = todo;
console.log(id); // 1함수에 사용
function printTodo(todo) {
console.log(`할일 ${todo.content}은 ${todo.completed ? '완료' : '비완료'} 상태입니다.`);
}
printTodo({ id: 1, content: 'HTML', completed: true });
function printTodo({ content, completed }) {
console.log(`할일 ${content}은 ${completed ? '완료' : '비완료'} 상태입니다.`);
}
printTodo({ id: 1, content: 'HTML', completed: true });rest 프로퍼티
const { x, ...rest } = { x: 1, y: 2, z: 3 };
console.log(x, rest); // 1 { y: 2, z: 3 }Set과 Map
Set
Set 객체는 중복되지 않는 유일한 값들의 집합이다. Set 객체는 배열과 유사하지만 다르다. 중복x, 순서x, 인덱스 접근x
Set 생성자 함수는 이터러블을 인수로 전달받아 Set 객체를 생성한다. 이때 이터러블의 중복된 값은 Set 객체에 요소로 저장되지 않는다.
중복제거
// 배열의 중복 요소 제거
const uniq = array => array.filter((v, i, self) => self.indexOf(v) === i);
console.log(uniq([2, 1, 2, 3, 4, 3, 4])); // [2, 1, 3, 4]
// Set을 사용한 배열의 중복 요소 제거
const uniq = array => [...new Set(array)];
console.log(uniq([2, 1, 2, 3, 4, 3, 4])); // [2, 1, 3, 4]size : 요소 개수 확인
add : 요소 추가. .add(1).add(2) 가능
has : 요소 존재 여부 확인
delete : 삭제 .delte(1).delete(2) 가능
clear : 일괄 삭제
forEach : 요소 순회. (현재 순회 중인 요소 값, 현재 순회 중인 요소 값,, 현재 순회 중인 Set 객체 자체)
for of : Set 객체는 이터러블이므로 순회 가능, 스프레드, 디스트럭처링 대상 가능
const set = new Set([1, 2, 3]);
// Set 객체는 Set.prototype의 Symbol.iterator 메서드를 상속받는 이터러블이다.
console.log(Symbol.iterator in set); // true
// 이터러블인 Set 객체는 for...of 문으로 순회할 수 있다.
for (const value of set) {
console.log(value); // 1 2 3
}
// 이터러블인 Set 객체는 스프레드 문법의 대상이 될 수 있다.
console.log([...set]); // [1, 2, 3]
// 이터러블인 Set 객체는 배열 디스트럭처링 할당의 대상이 될 수 있다.
const [a, ...rest] = [...set];
console.log(a, rest); // 1, [2, 3]교집합
Set.prototype.intersection = function (set) {
return new Set([...this].filter(v => set.has(v)));
};합집합
Set.prototype.union = function (set) {
return new Set([...this, ...set]);
};차집합
Set.prototype.difference = function (set) {
return new Set([...this].filter(v => !set.has(v)));
};부분 집합과 상위 집합
Set.prototype.isSuperset = function (subset) {
const supersetArr = [...this];
return [...subset].every(v => supersetArr.includes(v));
};Map
Map 객체는 키와 쌍으로 이루어진 컬렉션이다. 객체와 유사하지만 다르다. 객체를 포함한 모든 값을 키로 사용 가능, 이터러블, 개수 확인 size
const map1 = new Map([['key1', 'value1'], ['key2', 'value2']]);
console.log(map1); // Map(2) {"key1" => "value1", "key2" => "value2"}
const map2 = new Map([1, 2]); // TypeError: Iterator value 1 is not an entry object
const map = new Map([['key1', 'value1'], ['key1', 'value2']]);
console.log(map); // Map(1) {"key1" => "value2"}size : 요소 개수
set : 요소 추가
get : 요소 취득
has : 존재 여부 확인
delete : 요소 삭제
clear : 요소 일괄 삭제
forEach : 요소 순회 (현재 순회중인 요소값, 요소 키, Map 객체)
for of : 이터러블이므로 가능. 스프레드, 배열 디스트럭처링 할당의 대상 가능
const lee = { name: 'Lee' };
const kim = { name: 'Kim' };
const map = new Map([[lee, 'developer'], [kim, 'designer']]);
// Map 객체는 Map.prototype의 Symbol.iterator 메서드를 상속받는 이터러블이다.
console.log(Symbol.iterator in map); // true
// 이터러블인 Map 객체는 for...of 문으로 순회할 수 있다.
for (const entry of map) {
console.log(entry); // [{name: "Lee"}, "developer"] [{name: "Kim"}, "designer"]
}
// 이터러블인 Map 객체는 스프레드 문법의 대상이 될 수 있다.
console.log([...map]);
// [[{name: "Lee"}, "developer"], [{name: "Kim"}, "designer"]]
// 이터러블인 Map 객체는 배열 디스트럭처링 할당의 대상이 될 수 있다.
const [a, b] = map;
console.log(a, b); // [{name: "Lee"}, "developer"] [{name: "Kim"}, "designer"]Map 객체는 이터러블이면서 동시에 이터레이터인 객체를 반환하는 메서드를 제공한다.
keys, values, entries
const lee = { name: 'Lee' };
const kim = { name: 'Kim' };
const map = new Map([[lee, 'developer'], [kim, 'designer']]);
// Map.prototype.keys는 Map 객체에서 요소키를 값으로 갖는 이터레이터를 반환한다.
for (const key of map.keys()) {
console.log(key); // {name: "Lee"} {name: "Kim"}
}
// Map.prototype.values는 Map 객체에서 요소값을 값으로 갖는 이터레이터를 반환한다.
for (const value of map.values()) {
console.log(value); // developer designer
}
// Map.prototype.entries는 Map 객체에서 요소키와 요소값을 값으로 갖는 이터레이터를 반환한다.
for (const entry of map.entries()) {
console.log(entry); // [{name: "Lee"}, "developer"] [{name: "Kim"}, "designer"]
}
'책 > 모던 자바스크립트 Deep Dive' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 모던자바스크립트 10(40장~41장) (이벤트, 타이머 ) (0) | 2021.05.21 |
|---|---|
| 모던자바스크립트 10(38장~39장) (브라우저의 렌더링, DOM) (0) | 2021.05.18 |
| 모던자바스크립트 8(28장~33장) (0) | 2021.05.11 |
| 모던자바스크립트 7(27장) 배열 (0) | 2021.05.11 |
| 모던자바스크립트 6(25장~26장) (클래스, es6함수) (0) | 2021.04.26 |
